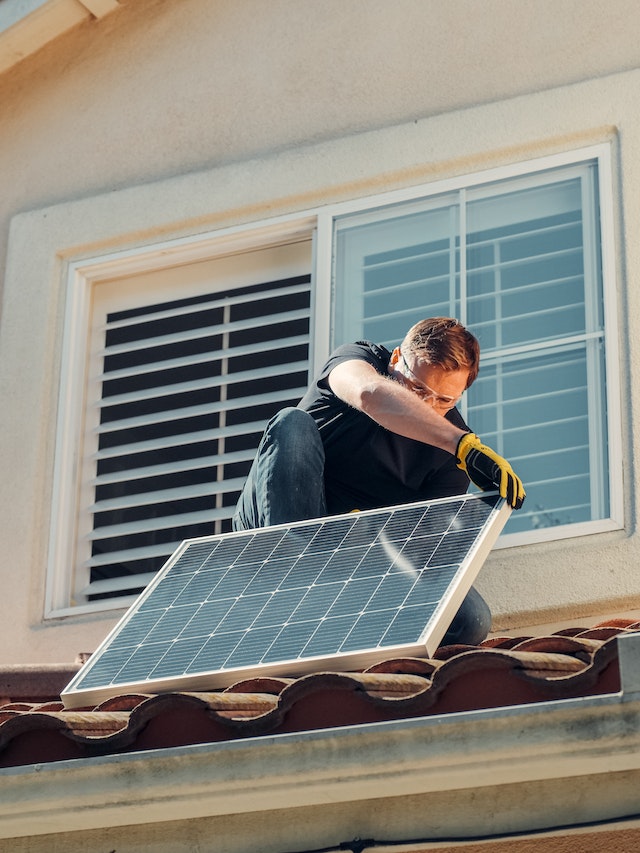
The sun is a powerful and constant source of energy, and harnessing its power through solar panels is becoming an increasingly popular way to generate electricity. Unlike fossil fuels, solar energy is a clean and renewable resource that does not contribute to harmful emissions or pollute the environment. By taking advantage of solar power, we can reduce our reliance on non-renewable sources of energy and make a positive impact on the planet.
As the demand for clean energy continues to grow, advancements in solar technology are making it even more efficient and affordable. With the potential to greatly reduce our carbon footprint and provide energy independence, solar power is a wise investment for both the environment and our wallets.
How do solar panels work?
Here is how solar panels work from a technical perspective:
Solar panels are made up of photovoltaic (PV) cells, which convert sunlight into direct current (DC) electricity. The PV cells are made up of silicon, a semiconducting material that absorbs sunlight and releases electrons. Silicon is a common element. Most of it is sand!
The electrons are then collected by metal conductors and passed through wiring to an inverter, which converts the DC electricity into usable alternating current (AC) electricity. The AC electricity is then sent to the building’s electrical panel, where it can be used to power appliances and devices.
Excess energy can also be sent back to the power grid, earning credits or money for the homeowner through net metering programs. Overall, solar power offers numerous benefits for the environment, energy independence, and cost savings. As we continue to invest in this renewable resource, we’re not only making a smart financial decision, but we’re also doing our part to create a more sustainable and clean future for all.
Types of Solar Power Systems
Grid-Tied Solar Systems: The most common type of solar power system, grid-tied systems are connected to the utility grid. These systems allow for the seamless integration of solar power with the existing power grid, ensuring a constant supply of electricity. Excess energy produced by the solar panels can be fed back into the grid, earning credits or reducing the homeowner’s electricity bill. Grid-tied systems do not require batteries for energy storage, which reduces costs and maintenance.
Off-Grid Solar Systems: Off-grid systems are designed to operate independently from the utility grid. These systems are ideal for remote locations without access to electricity or for individuals seeking complete energy independence. Off-grid systems require battery banks to store excess energy generated during the day, which can be used during nighttime or cloudy days. Proper sizing and maintenance of battery systems are crucial for reliable off-grid solar power.

Hybrid Solar Systems: Hybrid systems combine the best features of both grid-tied and off-grid systems. These systems are connected to the utility grid like grid-tied systems but also incorporate battery storage like off-grid systems. Hybrid systems provide backup power during grid outages, ensuring a continuous supply of electricity. Excess energy can be stored in batteries for later use or fed back into the grid.
Solar Water Heating Systems: Solar water heating systems utilize the sun’s energy to heat water for household or commercial use. These systems are typically composed of solar collectors, storage tanks, pumps, and control systems. Solar water heating systems can significantly reduce energy consumption and save money on heating bills. They are particularly effective in regions with ample sunlight and high water heating demands.
Concentrated Solar Power (CSP) Systems: Concentrated solar power systems focus sunlight onto a small area using mirrors or lenses. The concentrated sunlight generates heat, which is then used to produce steam that drives a turbine to generate electricity. CSP systems are suited for large-scale power production and can incorporate thermal energy storage to provide electricity even after sunset. These systems are often used in utility-scale projects and can provide consistent power output.
Choosing the right type of solar power system depends on various factors, including energy needs, location, budget, and long-term goals. Consulting with solar power professionals can help determine the best system for individual requirements. Whether it’s a grid-tied system for reducing electricity bills or an off-grid system for self-sufficiency, solar power offers a wide range of options to meet diverse energy needs.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Solar Power
When considering the adoption of solar power, it is important to weigh the advantages and disadvantages to make an informed decision. Here are some key points to consider:
Advantages:
Renewable and Clean: Solar power harnesses energy from the sun, a virtually infinite resource. Unlike fossil fuels, solar energy does not produce greenhouse gas emissions, air pollution, or contribute to climate change.
Cost Savings: Although the initial installation cost of solar panels can be high, they provide long-term cost savings. By generating your own electricity, you can reduce or eliminate monthly energy bills.
Energy Independence: With solar power, you become less reliant on the conventional power grid. This provides a sense of security, particularly during power outages or emergencies.
Versatile Installation: Solar panels can be installed on various surfaces such as rooftops, ground mounts, and even integrated into building materials. This versatility allows for their use in diverse settings, both residential and commercial.
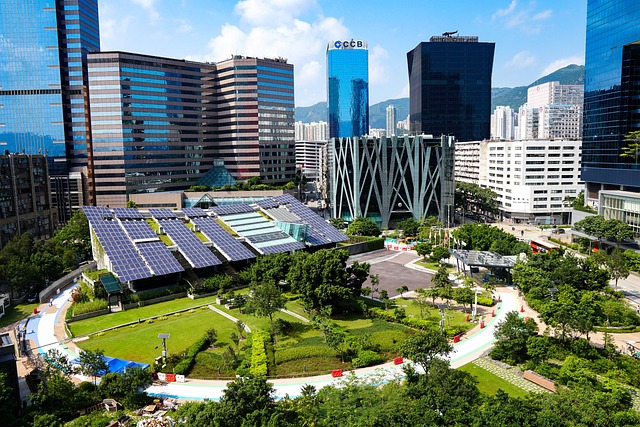

Versatile Installation: Solar panels can be installed on various surfaces such as rooftops, ground mounts, and even integrated into building materials. This versatility allows for their use in diverse settings, both residential and commercial.
Government Incentives: Many governments and utilities offer incentives and tax credits to encourage the use of solar power. These financial benefits make solar installations more accessible and affordable.
Disadvantages:
High Initial Costs: The cost of purchasing and installing solar panels can be substantial, which may deter some individuals or businesses from adopting solar power.
Weather Dependence: The amount of electricity produced by solar panels is affected by weather conditions. On cloudy or rainy days, the energy production may decrease, potentially resulting in lower electricity generation.
Limited Efficiency: Solar panels have a limit to their efficiency in converting sunlight into electricity. While advancements in technology have improved efficiency, there is still room for further development.
Land and Space Requirements: In some cases, solar installations may require a significant amount of space, making it challenging for those with limited area available.
Maintenance and Lifespan: Solar panels require regular maintenance, including cleaning and monitoring for any issues. Additionally, they have a limited lifespan, typically around 25-30 years, and may require replacement afterward.
Global Solar Power Trends
Increasing Adoption: Solar power has witnessed a remarkable growth trajectory in recent years, with an increasing number of countries and individuals embracing this renewable energy source. The global solar capacity has been rapidly expanding, contributing significantly to the global electricity mix.
Developing Markets: Emerging markets such as China, India, and Brazil have experienced a surge in solar installations as they seek to meet their growing energy demands sustainably. These countries have been investing heavily in solar infrastructure, leading to a substantial increase in solar power generation.

Developing Markets: Emerging markets such as China, India, and Brazil have experienced a surge in solar installations as they seek to meet their growing energy demands sustainably. These countries have been investing heavily in solar infrastructure, leading to a substantial increase in solar power generation.
Technological Advancements: Continuous innovation and research in solar technology have led to improved efficiency and cost-effectiveness. Breakthroughs in materials, design, and manufacturing techniques have made solar panels more efficient, durable, and affordable, making solar power an increasingly attractive option.
Grid Parity: The concept of grid parity, where the cost of generating electricity from solar power becomes equal to or cheaper than traditional energy sources, has become a reality in many regions. This milestone has significantly contributed to the widespread adoption of solar power as a viable energy solution.
Large-Scale Projects: Utility-scale solar projects, also known as solar farms or solar parks, are being developed across the globe. These large-scale installations can generate massive amounts of clean energy, helping countries transition to more sustainable power sources.
Rooftop Solar: Residential and commercial rooftop solar installations have also experienced a surge in popularity. Individuals and businesses are choosing to generate their own electricity, reducing their reliance on the grid and saving money on energy bills.
Energy Storage Integration: The integration of energy storage technology with solar power systems has gained momentum. Energy storage solutions, such as batteries, allow for the capture and storage of excess solar energy generated during the day, which can be utilized in evenings or during periods of low sunlight.

Floating Solar: Floating plants are gaining traction, particularly in regions with limited available land. These installations, erected on bodies of water, maximize the use of space and provide an efficient solution for solar power generation.
International Collaboration: Governments, organizations, and institutions worldwide are collaborating to promote solar power adoption.
International agreements and initiatives aim to accelerate the deployment of solar projects, exchange best practices, and support research and development.
Off-Grid Solutions: In remote areas without access to electricity grids, solar power offers a lifeline. Off-grid solar solutions, such as portable solar panels and solar-powered microgrids, have the potential to bring electricity to underserved communities, transforming lives and empowering individuals.
Solar Power in Transportation: Solar power is expanding beyond electricity generation and making its way into the transportation sector. Solar-powered vehicles, including cars, buses, and even airplanes, are being developed, showcasing the versatility and potential of solar energy.
Environmental Consciousness: Growing concerns about climate change and environmental degradation have propelled the adoption of solar power. Individuals, businesses, and governments are recognizing the importance of reducing carbon emissions and embracing clean energy alternatives like solar power.
As the world continues to prioritize a sustainable future, solar power is poised to play an increasingly significant role in meeting global energy needs. With ongoing advancements in technology and growing public awareness,it has the potential to transform the way we generate and consume electricity, providing a cleaner, more sustainable world for future generations.