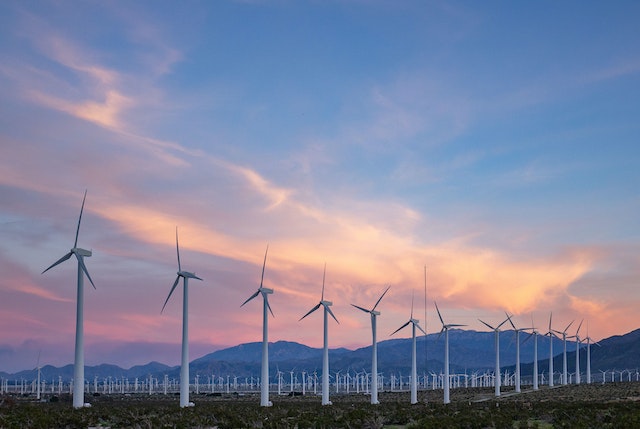
Wind power has become a popular source of energy in recent years, providing clean and renewable power for homes and businesses alike. The massive turbines used for wind farms can generate enough electricity to power entire cities, and their sleek blades slicing through the air are a beautiful sight to behold.
But the use of wind to generate energy is nothing new. Centuries ago, windmills were used to grind grain and pump water. These humble structures were much simpler than the high-tech turbines we see today, but they paved the way for the development of modern wind power.
As the world faces the ever-increasing threat of climate change, the need for renewable energy sources has never been greater. Wind power is a key part of the solution, providing a clean and sustainable alternative to fossil fuels. And as technology continues to evolve, the potential of this powerful resource only grows.
How Wind Energy is Harnessed
Harnessing the power of the wind requires more than just a strong gust. It requires advanced technology and engineering to efficiently convert that energy into usable electricity. Today, wind energy is a vital part of the renewable energy sector and a key solution to combatting climate change. Wind energy is harvested through the use of advanced technology, primarily wind turbines.
Wind Turbines
The transformation of wind into usable electricity is a marvel of engineering and ingenuity. Modern wind turbines have evolved into sophisticated machines that harness the power of the wind in a highly efficient and elegant manner.
Rotor
At the heart of a wind turbine are its rotor blades. Made from durable materials like fiberglass or carbon composites, the blades are designed to capture the kinetic energy of the wind. The blades are connected to a central hub, which transfers the rotational energy to the nacelle.
Nacelle
The housing atop the towering tower, inside the nacelle, a gearbox increases the rotational speed of the blades, optimizing power generation. The kinetic energy from the blades is converted into electrical energy by a generator located within the nacelle.
To enhance their performance, wind turbines are equipped with advanced control systems. These systems, comprised of sensors and computer algorithms, continually monitor wind conditions and adjust the position and orientation of the turbine for optimal energy production. By closely tracking wind patterns, the control system ensures that the blades capture as much energy as possible, even in varying wind speeds.
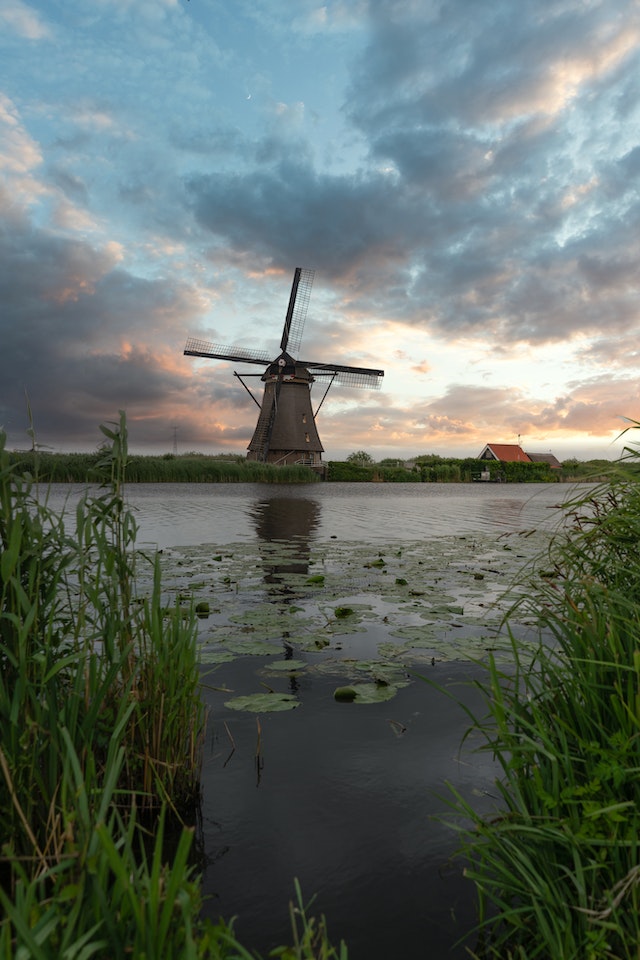

Tower
The tower that supports the wind turbine plays a crucial role in maximizing its efficiency. Taller towers are preferred as they allow the turbines to access stronger, more consistent winds at higher altitudes. Towers are constructed using sturdy materials like steel or concrete to ensure stability and longevity, even in harsh weather conditions.
Onshore Wind Farms
Onshore wind farms are designed to tap into the wind resources available on land. These clusters of wind turbines, strategically placed in areas with favorable wind conditions, work together to generate electricity for local communities. The electricity generated by the turbines is transported through an electrical grid, distributing power where it is needed.
Offshore Wind Farms
Offshore wind farms, on the other hand, take advantage of the strong and consistent winds found at sea. Innovations in wind energy technology now allow turbines to be anchored to the seabed using cables, enabling the utilization of deeper waters. Subsea cables transmit the electricity generated offshore to the mainland, integrating the wind farm with the power grid.
Innovations and Advancements
The wind energy sector is continually evolving, with advancements focused on improving efficiency and reducing costs.
Aerodynamics: Ongoing research has led to the development of more aerodynamic blade designs. This improves overall turbine efficiency, allowing for increased energy production even in lower wind speeds.
Energy Storage Solutions: To address the intermittent nature of wind power, innovative storage solutions, such as large-scale batteries and pumped hydro storage, are being integrated with wind farms.
Digitalization and AI: Smart technologies and artificial intelligence are playing a crucial role in optimizing wind energy operations, enabling real-time data monitoring, predictive maintenance, and enhanced turbine performance.
The convergence of these technological advancements has propelled wind energy forward, transforming it into a formidable source of clean and sustainable power. As wind turbines rotate gracefully in the breeze, they symbolize humanity’s commitment to a greener future. With continued research and investments in wind energy technology, the potential for a world powered by the wind is boundless.
Advantages and Benefits of Wind Power
Clean and Sustainable Energy Source
Wind power is a renewable energy source, meaning it will not deplete over time. It produces no greenhouse gas emissions or air pollutants, making it an environmentally friendly alternative to fossil fuels. Harnessing wind energy helps reduce our dependency on finite resources and mitigates the impact of climate change.

Abundant and Widely Available Resource
Wind is a globally available resource, with potential for harnessing in various regions. Coastal areas, open plains, and mountain passes are particularly well-suited for wind power generation. As long as the wind blows, we have access to this vast and inexhaustible energy source.
Economic Benefits and Job Creation
Wind power installations contribute to local economies through job creation, both during the construction phase and for ongoing maintenance and operation. The wind energy industry stimulates economic growth and attracts investments, creating a ripple effect throughout supply chains and ancillary services.
Energy Independence and Security
Utilizing wind power helps diversify energy sources, reducing reliance on imported fossil fuels. Wind energy reduces vulnerabilities associated with fluctuating fuel prices and geopolitical conflicts, promoting energy independence and national security.
Community Development and Social Impact
Wind power projects often engage local communities, providing opportunities for collaboration and cooperation. Revenue-sharing programs and community benefit agreements can provide financial benefits to nearby communities, supporting local infrastructure and social programs.
Scalability and Adaptability
Wind power is scalable to various project sizes, from small-scale installations to large wind farms. On land or offshore, wind projects can be tailored to suit specific geographic and environmental conditions, making it a versatile solution for diverse energy needs.
Public Health Benefits
Wind energy production does not release harmful pollutants into the air, resulting in improved air quality and reduced respiratory ailments. Minimizing the use of fossil fuels for electricity generation reduces the associated health risks, benefiting both local communities and the global population.
Resilience and Disaster Resistance
Unlike centralized power plants, wind turbines can be distributed across a wide geographical area, making the power grid more resilient to natural disasters and extreme weather events. Decentralizing energy production through wind power increases grid stability and reduces the likelihood of widespread electricity outages.
Long-Term Cost Savings
Once installed, wind turbines have relatively low operational and maintenance costs. As technology advances and economies of scale are realized, the cost of wind energy continues to decrease, making it an economically viable long-term investment.

Symbol of Progress and Innovation
Wind turbines have become iconic symbols of progress and sustainability, inspiring communities and individuals to embrace clean energy solutions. Embracing wind power demonstrates a commitment to a greener future and inspires innovation in renewable energy technologies.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
As our world grapples with the challenges of climate change and environmental degradation, it is crucial to evaluate the environmental impact and the sustainability of our energy sources. In this section, we delve into the environmental implications of wind power and its contribution to a greener and more sustainable future.
Minimal Carbon Footprint
One of the most significant advantages of wind power is its minimal carbon footprint. Unlike fossil fuel-based energy sources, wind turbines do not release greenhouse gases, such as carbon dioxide, methane, or nitrous oxide, into the atmosphere. By harnessing the wind’s energy, we can significantly reduce our carbon emissions and mitigate climate change’s devastating effects.
Preservation of Air Quality
Wind energy does not contribute to air pollution since it does not release harmful pollutants such as sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, or particulate matter. This has a tangible impact on public health, as the reduction in air pollutants leads to improved air quality, reducing the risk of respiratory diseases and other health issues associated with poor air quality.
Biodiversity Conservation
When properly planned and managed, wind power projects can have minimal impact on wildlife and their habitats. By avoiding sensitive ecological areas, such as migratory bird routes or critical habitats, wind farms can minimize their impact on biodiversity. Additionally, design modifications, such as reducing blade rotation speeds during periods of high bird activity, help further mitigate potential risks to avian life.

Land Utilization and Ecosystem Restoration
One criticism often raised against wind power is the land utilization required for wind farms. However, it is essential to note that wind turbines can coexist with other land uses, such as agriculture or grazing, creating opportunities for shared land utilization. Moreover, by repurposing unused or degraded land for wind farms, we can contribute to ecosystem restoration, enhancing biodiversity and ecological functionality.
Water Conservation
Unlike conventional power plants, wind energy production requires minimal water consumption. Traditional power generation relies heavily on water for cooling processes, resulting in significant water consumption and withdrawal from natural sources. Wind power eliminates these water demands, contributing to the conservation and sustainable management of this precious resource.
Noise Pollution Considerations
While wind turbines generate sound during operation, modern technology and careful design practices have significantly minimized potential noise pollution. Advanced engineering techniques and proper siting help ensure that sound emissions from turbines are within acceptable limits, preserving the tranquility of nearby communities and habitats.
Lifecycle Analysis and End-of-Life Recycling
To fully understand the sustainability of wind power, a comprehensive lifecycle analysis is essential. While wind turbines have a finite lifespan, typically ranging from 20 to 25 years, their materials can be recycled. This promotes a circular economy approach, reducing waste and minimizing the environmental impact of turbine decommissioning.
Synergy with Other Renewable Energy Sources
Wind power synergizes well with other renewable energy sources, such as solar power, hydropower, and geothermal energy. Combining these sources in a diversified energy portfolio ensures a more reliable and consistent power supply. By diversifying our energy mix, we reduce the dependence on any single energy source and enhance overall energy resilience.
Striving for Continuous Improvement
The wind energy industry is committed to continuous improvement, seeking innovative solutions to address any existing environmental challenges. Ongoing research and development focus on optimizing turbine design, reducing material consumption, and improving recycling practices. With each technological advancement, wind power becomes even more sustainable and environmentally friendly.
Wind power offers a promising path towards a sustainable and eco-friendly future. With its minimal carbon footprint, preservation of air quality, biodiversity conservation efforts, and land utilization considerations, wind energy is joining forces with other renewable energy sources to meet our energy needs while minimizing environmental impact. As we strive towards a greener and more sustainable planet, wind power plays a crucial role in mitigating climate change and protecting our natural resources for future generations.